Short Course on R Tools
Introduction to Rcpp
Marquette University
SCoRT - Summer 2025
Outline
- Motivation & Introduction
- Getting Started with
evalCpp()&cppFunction() - Using
sourceCpp() - Data Types & Conversions
- Standard Template Library (STL)
- Using Rcpp in Packages
- Advanced Topics & Resources
Motivation & Introduction
- Performance Bottlenecks: loops, recursion, complex operations
- Rcpp: smooth bridge between R and C++
- Do things you could not do before
Advantages:
- Low overhead function calls
- Access to STL (data structures & algorithms)
- Cleaner, maintainable code
Basic Usage: evalCpp()
evalCpp()evaluates a single C++ expression. Includes and dependencies can be declared.This allows us to quickly check C++ constructs.
Simple Example
- R Version of ‘is this number odd or even’
Simple Example - Using cppFunction()
- Rcpp Version of ‘is this number odd or even’
Rcpp::cppFunction("
bool isOdd_cpp(int num = 10) {
bool result = (num % 2 == 1);
return result;
}")
c(isOdd_cpp(42L), isOdd_cpp(43L))
># [1] FALSE TRUE- Use
cppFunction()in R console or script - Fast prototyping & testing
- Good for small functions
Second Example: VAR(1)
Let’s consider a simple possible \(VAR(1)\) system of \(k\) variables.
For \(k = 2\):
\[ X_t = X_{t-1} B + E_t \]
where \(X_t\) is a row vector of length \(2\), \(B\) is a \(2×2\) matrix, and \(E_t\) is a row of the error matrix of \(2\) columns.
Second Example: VAR(1)
In R (C++) code, given both the coefficient and error matrices:
Second Example: VAR(1)
Rcpp::cppFunction('arma::mat cppSim(arma::mat B, arma::mat E) {
int m = E.n_rows, n = E.n_cols;
arma::mat X(m, n);
X.row(0) = arma::zeros<arma::mat>(1, n);
for (int r = 1; r < m; r++) {
X.row(r) = X.row(r-1) * B + E.row(r);
}
return X;
}', depends="RcppArmadillo")
a <- matrix(c(0.5, 0.1, 0.1, 0.5), nrow = 2)
e <- matrix(rnorm(10000), ncol = 2)
rbenchmark::benchmark(cppSim(a, e), rSim(a, e), order="relative")[, 1:4]
># test replications elapsed relative
># 1 cppSim(a, e) 100 0.010 1.0
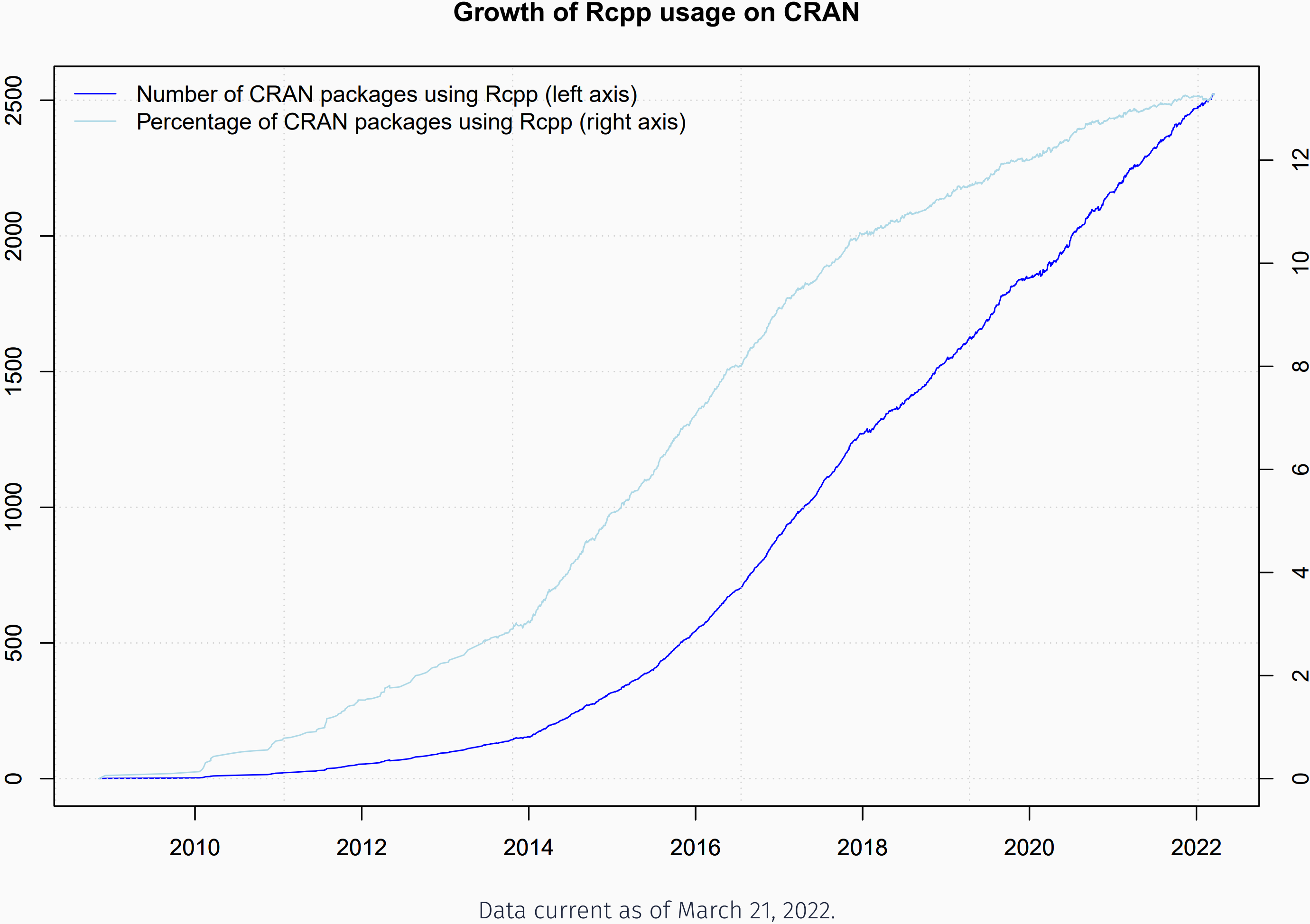
># 2 rSim(a, e) 100 0.728 72.8Growth of Rcpp
- Sometimes speed is not the only reason
- Easy access to C/C++ libraries
- C & C++ provide numerous libraries + APIs
- Easy to provide access to as Rcpp eases data transfer
- Rcpp is currently used by
- 3053 CRAN packages
- 250+ BioConductor packages
- an unknown (but “large”) number of GitHub projects
Pagerank
#remotes::install_github("https://github.com/andrie/pagerank.git")
suppressMessages(library(utils))
library(pagerank)
cran <- "https://cloud.r-project.org"
pr <- compute_pagerank(cran)
round(100 * pr[1:5], 3)
># Rcpp ggplot2 dplyr MASS magrittr
># 2.744 1.516 1.274 1.122 0.814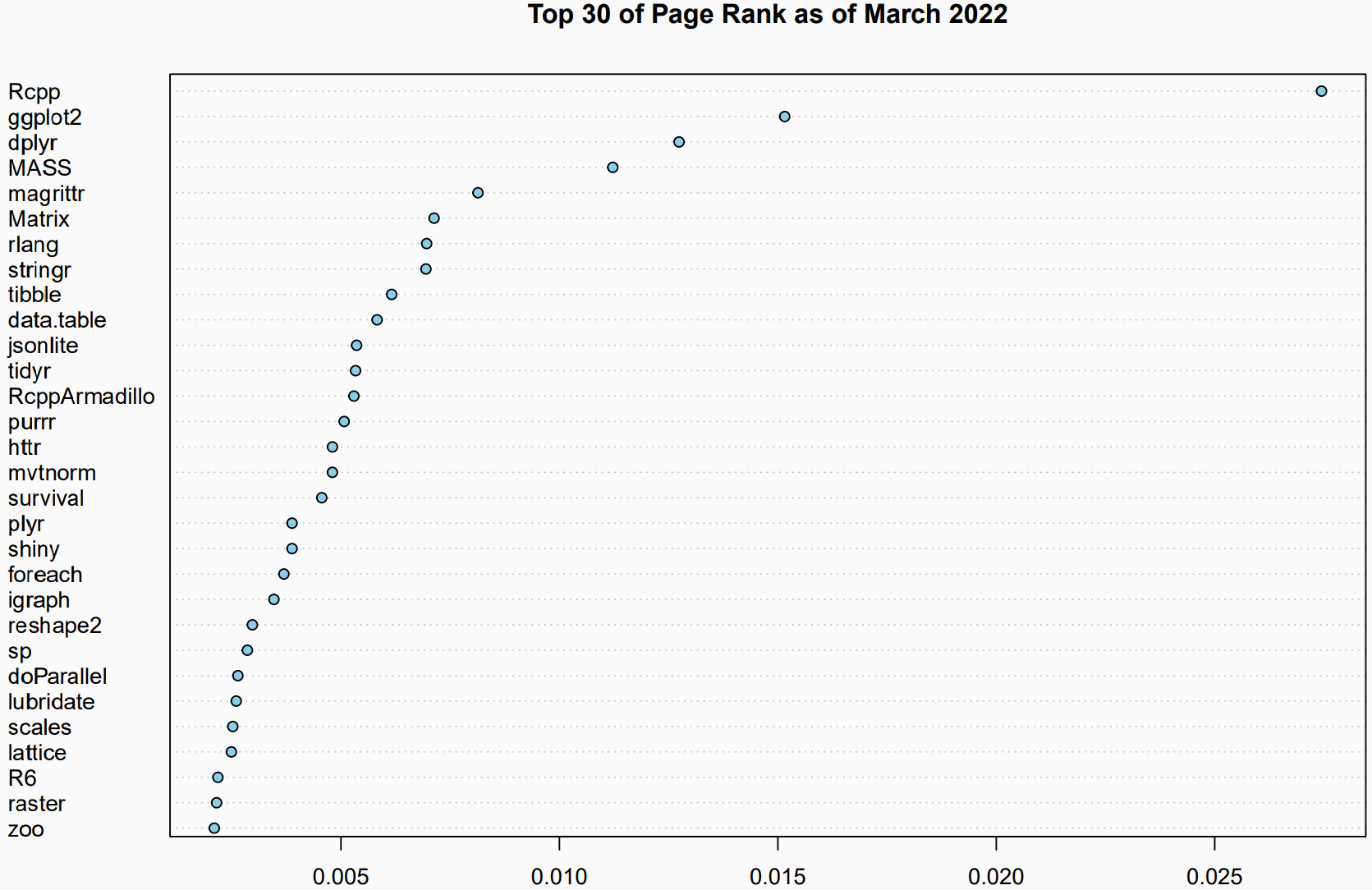
Percentage of Compiled Packages
db <- tools::CRAN_package_db() # added in R 3.4.0
db <- db[!duplicated(db[, 1]), ] # rows: number of packages
nTot <- nrow(db) # columns: different attributes
nRcpp <- length(tools::dependsOnPkgs("Rcpp", recursive = FALSE, installed = db))
nCompiled <- table(db[, "NeedsCompilation"])[["yes"]]
propRcpp <- nRcpp / nCompiled * 100
data.frame(tot = nTot, totRcpp = nRcpp, totCompiled = nCompiled,
RcppPctOfCompiled = propRcpp)
># tot totRcpp totCompiled RcppPctOfCompiled
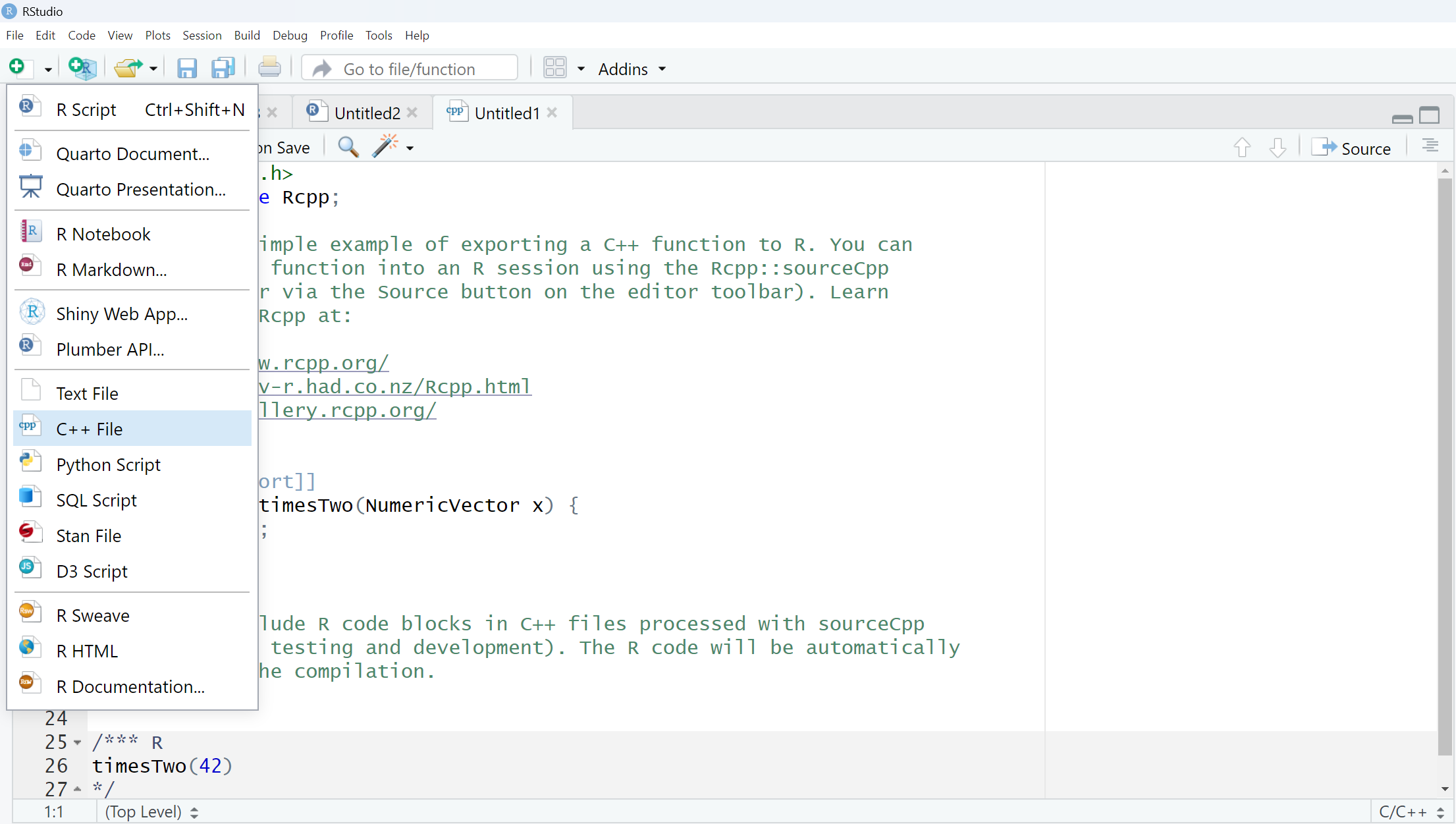
># 1 22501 3053 4981 61.29291Rcpp in Rstudio - Using sourceCpp()
Create standalone
.cppfiles with:
Using sourceCpp()
- So what just happened?
- We defined a simple C++ function
- It operates on a numeric vector argument
- We ask Rcpp to ‘source it’ for us
- Behind the scenes Rcpp creates a wrapper
- Rcpp then compiles, links, and loads the wrapper
- The function is available in R under its C++ name
- We defined a simple C++ function
- Benefits:
- Editor support (syntax highlighting)
- Easier debugging & error tracking
Another Example: Focus on Speed
Consider a function defined as
\[ f(n) = \begin{cases} n & \text{when } n < 2 \\ f(n-1) + f(n-2) & \text{when } n \ge 2 \end{cases} \] that creates Fibonacci sequence. The R implementation and use:
Another Example: Timing R Implementation
- The R implementation:
Another Example: C++ Implementation
Another Example: Comparing Timing
- Rcpp implementation:
- Timing:
- A nice gain of a few orders of magnitude.
Data Types & Conversions
R vectors ↔︎ C++ classes:
NumericVector,IntegerVector,CharacterVector,LogicalVector
Scalars:
double,int,String,boolKey methods:
.size(),.begin(),.end()- Constructors:
NumericVector out(n)
Types
R Type mapping:
- Standard R types (integer, numeric, list, function, … and compound objects) are mapped to corresponding C++ types:
library(Rcpp)
cppFunction("NumericVector logabs(NumericVector x) {
return log(abs(x));
}")
logabs(seq(-5, 5, by = 2))
># [1] 1.609438 1.098612 0.000000 0.000000 1.098612 1.609438- Vectorized C++! Here
log(abs())runs directly on vectors as R would.
STL Type Mapping
code/logabs2.cpp
Not vectorized but ‘sweeps’ f() along std::vector<double> via STL std::transform().
Hands-on Exercises (30 min)
Using Rcpp in Packages
Add to package:
LinkingTo: Rcppin DESCRIPTIONuseDynLib(pkg)&importFrom(Rcpp, sourceCpp)in NAMESPACE
usethis::use_rcpp()automates setupRun
Rcpp::compileAttributes()to generate bindingsThirteen Simple Steps Vignette by Dirk Eddelbuettel
Advanced Topics & Resources
- Attributes vignette:
vignette('Rcpp-attributes') - Modules: expose C++ classes to R
- RcppGSL, RcppArmadillo for specialized libraries
- Books: Effective C++, Effective STL
- Online: Rcpp homepage, mailing list
Summary & Q&A

- Key takeaways:
- Profile before optimizing
- Inline vs file-based workflows
- Master data conversions & STL
- Questions?
